1-What is the difference between a dentist and a pediatric dentist?
A pediatric dentist is trained specifically for several years and its daily practice is exclusively for child care, from an early childhood through adolescence. A pediatric dentist is concerned with the prevention, early detection and treatment of dental caries in children. It seeks to establish a relationship of trust with the child, to make a positive experience during their non-traumatic contact with the dental profession, so that it can continue throughout his adult life.
 Our goal is to help children grow up with healthy teeth and mouth, by teaching your children good oral habits that will last a lifetime.
Our goal is to help children grow up with healthy teeth and mouth, by teaching your children good oral habits that will last a lifetime.
2 – At what age should children see a pediatric dentist?
The first dental checkup for a child should be held one year or six months after the eruption of the first primary tooth.
Age 1: First review
Age 2: Second Review
Age 3: Review PLUS the first treatment for cleaning and fluoride.
3-How important is the first visit?
At the first appointment, your pediatric dentist will discuss the use of food hygiene measures (brushing, toothpaste, etc. …), silk evaluate fluoride needs and inform you about the different habits to adopt for prevention of dental caries and malocclusion in children.
Some dental problems specific to the child such as baby bottle tooth decay can easily be prevented, to a review a year be able to detect and prevent such problems. In most cases, early treatment of this type of decay can prevent more serious dental problems in the future.
5-What is the frequency of inspections and hygiene in children?
Control, every six months is recommended for children.In fact, tooth decay can progress rapidly in children, without symptoms or pain. However the frequency of monitoring should be adapted according to the caries risk of the child. Children who have dental caries and poor oral hygiene are more often recalled. The risk is assessed at each visit.
6-What will the visits of recall?
To raise your child good dental hygiene, ensuring `s good dental health.
To check if the baby teeth fall at the right time so that the adult tooth `s up well on the jaw.
To prevent and intercept the various problems related to the growth of the jaws.
To check if the permanent teeth grow properly, follow their eruption and thus escape processing complex `orthodontics.
To qualify for `preventive treatment of pit and fissure sealants on permanent molars, and on this, as they emerge.
To treat decay early as in the `child tooth decay progresses rapidly and should be treated as` appeared in order to avoid future problems much more serious.
7 – Why are primary teeth (milk) are important?
Primary teeth healthy is important to chew, speak and smile. They also serve to maintain the `space` s adult teeth and guide them in a good position on the jaw.
8 – How to prevent tooth decay in children?
The establishment of good habits of oral hygiene and food from an early age prevents in most cases the occurrence of dental caries.
However, many children have multiple caries at an early age after a prolonged and frequent use of the bottle containing natural milk, fruit juice, other sweetened liquids or prolonged breastfeeding. This condition is called “baby bottle syndrome”
Therefore it is important to never let your child fall asleep with a bottle or breast.
It should also be careful with medicines, including syrups, homeopathic medicines and asthma that are high in sugar. Taking these drugs before bedtime can cause tooth decay.
Snacking throughout the day and the intake of beverages, soft drinks (Coca-Cola for example) is often a poor eating habits of today’s teenagers. They participate in the development of dental caries in permanent teeth.
In any case, it is essential to brush your teeth twice a day, morning and especially at night.
9 – What is `what` a parent can do to help the `child during visits to the dentist?
Let the dentist and his team the task of explaining and describing `dental treatment for your child. They will use the terms `that a child can understand and image processing steps according to their understanding. As a parent before the appointment you can simply tell your child that the dentist will count his teeth and brushes. If you bring your child into the treatment room, be a silent partner, leave the dentist directly interact and communicate with your child.
Consider the day of the appointment as a normal day, do not as a special day. Do you stay relaxed even before and during the visit of your child. A positive attitude on your part will help to maximize your child to have a positive experience.
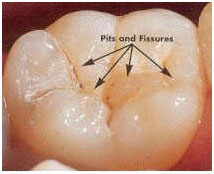
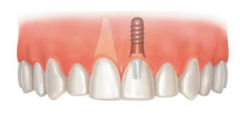
10 – What are pit and fissure sealants?
Molar non-protected
susceptible to decay Molar with Sealant
pit and fissure
Sealants are a protective barrier resin which is applied in pits and fissures of posterior teeth, protecting places most likely to decay.
Children are more likely than adults to develop tooth decay and should be sealed as soon as their back teeth which erupt (about 6 years).
The application of sealants is very easy for the` child. The process is quick and painless. Once applied, the life of sealants is 10 to 15 years.
11 – At what age should you start brushing children’s teeth?
At the onset of the first tooth, teeth cleaning should be done with a swab or a toothbrush “first age”. It is quite advisable to use a small amount of toothpaste (corresponding to small nail of the child) low-dose fluoride (250 ppm to 500 ppm). A As the evolution of the molars, you can increase the dosage of fluoride toothpaste. If your child does not take fluoride supplements (drops or tablets) you can use toothpaste dosed at 1000 ppm.
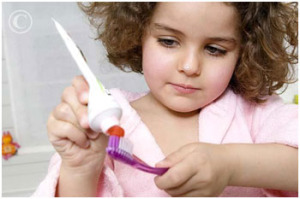
Brushing should be done by parents, twice a day, the morning after breakfast, and especially at night before bed. Parental control is essential until the age of 10-12 years.
12 – Should we give fluoride to children?
Fluoride plays a major role in preventing oral.
Fluoride is present in toothpastes, some bottled water, some salts and complementary inputs such as drops and tablets. The greater part of French territory, tap water is generally not fluoridated. The sources of fluoride are multiple, a review of fluoride intake must be completed before any prescription to avoid an overdose. A pediatric dentist may, after establishing this balance, adjust recommendations for fluoride to each patient.
In small amounts, fluoride is very beneficial:
It stabilizes and strengthens the enamel of teeth during and after mineralization, it greatly reduces the risk of caries.
But an excess of fluoride from all sources (ingestion of toothpaste for children who can not rinse mouth, overdose of fluoride drops or tablets, other inputs not detected by a fluorinated fluorinated balance) is harmful, it increases the risk of fluorosis is a defect of enamel, unsightly and safely, which is manifested by spots or white lines on the teeth. These spots can be more or less pronounced depending on the degree of fluorosis. If fluorosis is severe, the enamel often shows major malformations and brown spots.
13-What if the child sucks his thumb, a finger or a pacifier?
Thumb sucking, finger or pacifier is a common occurrence in young children, it is not a real problem before age 5. Risk is a malposition or malocclusion of the permanent teeth when they occur. We must as soon as possible to try to “replace” the thumb or finger in the nipple. Indeed, it is generally accepted that the decision of sucking of the teat is earlier when the social life of the child becomes more important. A pediatric dentist can encourage your child to do so. This recommendation and your determination with most children to easily stop sucking. However, if this approach is not effective, your dentist may recommend a brace to prevent suction.
14-Diseases
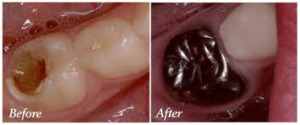
Cavities can change very quickly.
The pulpitis are fewer and shorter. They can occur without pain, much more frequently than in adults.
However abscesses of dental origin occur more easily in children than in adults.
Nursing bottle syndrome: syndrome called multiple bottle tooth decay occurring in young children (from 2 years), especially on the buccal surfaces of anterior teeth. These cavities are favored by: a prolonged breastfeeding, the permanent presence at bedtime or a bottle containing a sweet liquid, a limited oral hygiene.
15-Treatment
* Prevention by oral hygiene in pediatric dentistry
* Conservative Dentistry
Care decay are identical to those of the permanent tooth.
* Endodontics
However endodontic treatment differ.
* Pulpectomy: indicated in cases of total pulp inflammation or in the case of Le endodontic treatment is to remove the inflamed or necrotic pulp parenchyma and disinfect the root canal content. The root filling is made with a paste of zinc oxide eugenol. Indeed we will not do a root canal filling with gutta cones as the permanent teeth. The cones of gutta do not resolve and might block the root resorption.
* Pulpotomy: indicated in cases where the pulpal inflammation is localized to the pulp chamber, a pulpotomy (to the removal of the pulp canal pulp cameral preserve vital to the state or condition set)
Prosthesis *
On the prosthesis, when the tooth has a crown restoration when it is extended or endodontically treated, it must be protected by a ring called pedodontics preformed cap.
It can also make small resin removable appliances if several teeth were extracted early.